Meaning
A duty is an obligatory act , i.e. it is an act the opposite of which would be wrong. Thus duties and wrongs are generally co-related. The commission of a wrong is the breach of duty and the performance of duty is avoidance of wrong.
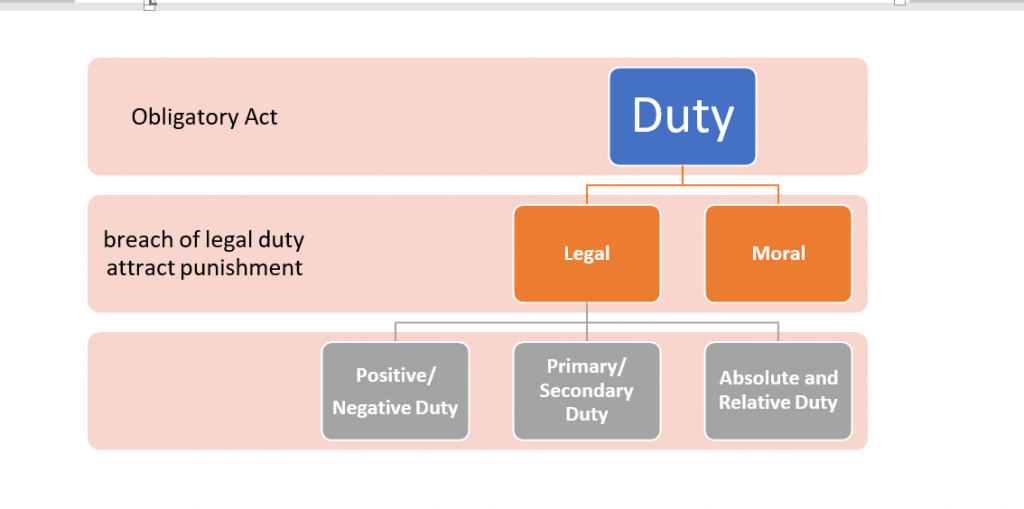
Duties has mainly two kinds
- Moral – Moral duty is not enforceable by state it is recognized by the society for the well being of its community.
- Legal : Legal duty has some statute which enables enforceability. Non performance of legal duty amounts to punishment.
Kinds of Duties
A duty may be moral but not legal or it may be legal but not moral or it may be both moral and legal at once. Legal duties can be subdivided as :
- Positive Duty : A positive duty implies some act on the part of the person on whom it is imposed. If a person owes money to another , the former is under a duty to pay the money to the latter. This is Positive Duty.
- Negative Duty :- A negative duty implies a forbearance on the part of the person on whom it is imposed . For example , if a person owns lands , other are under duty not to make any interference with that person’s use of the land. This is called negative duty.
- Primary and Secondary Duty : A primary duty is one which exists per se and is independent of any other duty . For instance, to forbear from causing personal injury to another is a primary duty.
A secondary duty, on the other hand, is one which has no independent existence but exists only for the enforcement of other duties . For example, a duty to pay damages for the injury done to a person, is secondary duty . A secondary duty is also called a sanctioning or remedial duty. - Absolute and Relative Duties : Absolutely duties are owed to the state breach of which is generally called a crime and the remedy for it is punishment.
Relative duties are owed to any person other than the one who imposing them, the breach of which is called civil injury which is redressing by compensation or restitution to the injured party .
Relation between Rights and Duties
1)Rights and Duties always go together:
Rights and duties are closely related and cannot be separated from one another. Both go side by side. These are the two sides of the same coin. If the state gives the right to life to a citizen, it also imposes an obligation on him to not to expose his life to dangers, as well as to respect the life of others. If I have a right to work and earn, it is also my duty to recognize the same right of others.
2)Right of One is the Duty of Others:
Rights can be enjoyed only in the world of duties. For every right there is corresponding duty. When the people fail to discharge their duties properly, the rights all become meaningless. “I can enjoy my rights only if the others allow me to do the same. I have” the right to life and it is the duty of others to respect my life and not to cause any harm to me.”
3)Rights of a Citizen also implies Duties for him:
Rights are not the monopoly of a single individual. Everybody gets these equally. This means that “others also have the same rights which I have, and it is my duty to see that others also enjoy their rights.” Laski has rightly said that one man’s right is also his duty. It is my duty to respect the rights of others as well as the duty to use my rights in the interest of society.
4)Rights are to be used for Social Good:
Rights originate in society. Therefore, while enjoying rights, we must always try to promote social interest. It is the duty of every one of us to use our rights for promoting the welfare of the society as a whole.
5.Duty towards the State:
Since state protects and enforces rights, it also becomes the duty of all citizens to be loyal to the state. It is their duty to obey the laws of the state and to pay taxes honestly. Citizens should always be ready to defend the state. Thus a citizen has both Rights and Duties. He enjoys rights and performs his duties. Rights and Duties are the two sides of the same coin.



