Introduction
Before discussing Provisions regarding health and welfare of workers under Factories Act, 1948 we must know who “Worker” is ? Worker means a person employed,
- directly or
- through any agency (including a contractor)
- with or without the knowledge of the principal employer,
- whether for remuneration or not
- in any manufacturing process, or
- in cleaning any part of the machinery or premises used for a manufacturing process, or
- in any other kind of work incidental to, or connected ‘with, the manufacturing process”
- or the subject of the manufacturing process but does not include any member of the armed forces of the Union.”-Sec. 2(1), as amended in 1976.
Explanation: Worker means any person engaged in any work connected with or incidental to a manufacturing process. Thus, the definition is wide. The term includes persons engaged directly and, also those who are engaged through an agency (including a contractor with or without the knowledge of the principal employer). The term includes clerical workers and persons paid by piece rates in a factory.
The term ‘worker’ does not include any member of the armed forces of Union.
Employment of the worker must be:
- in any manufacturing process
- in cleaning any part of the machinery or premises used for manufacturing process
- in any other kind of work incidental to or connected with the manufacturing process
PROVISIONS REGARDING THE HEALTH OF WORKERS
Sections 11 to 20 of the Factories Act, 1948 contain certain provisions intended to ensure that the conditions under which work is carried on in factories do not affect the health of the workers injuriously. The summary of the provisions are explained below:
Summary of the provisions of the Factories Act,1948 relating -to the health of workers are stated below.
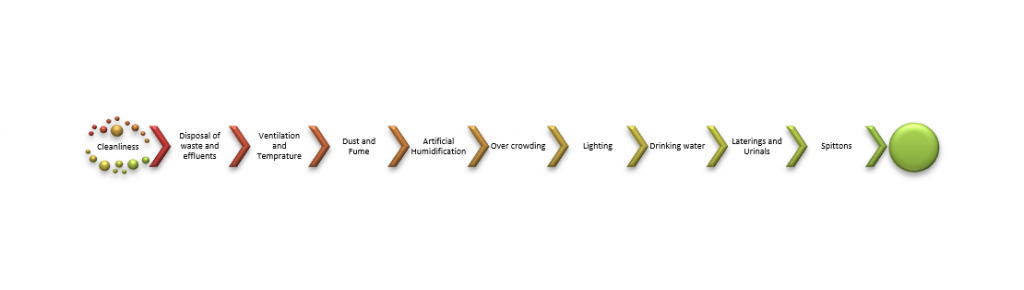
Cleanliness:
Every factory shall be kept clean and free from dirt, and the outflow of drains etc. The floors must be cleaned. Drainage shall be provided. Inside walls, partitions and ceilings must be repainted at least once in five years. When washable water paint is used they must be painted once every three years and washed at least every period of six months.-Sec. 11,’ as amended in 1976.
Disposal of wastes and effluents :
The waste materials produced from the manufacturing process must be effectively disposed off- Sec. 12.
Now it is mandatory upon every occupier to construct an Effluent Treatment Plant or a common Treatment Plant for 2 or more industries.
Ventilation and Temperature :
There must be provision for adequate ventilation by the circulation of fresh air: The temperature must be kept at a comfortable level. Hot parts of machines must be separated and insulated. -Sec. 13
Dust and Fume
If the manufacturing process used. gives off injurious or offensive dust and fume steps must be taken so that they are not inhaled or accumulated. The exhaust fumes of internal combustion engines must be conducted outside the factory.– Sec. 14.
Artificial humidification:
Humidity= Dampness, moisture. The water used for this purpose must be pure. It must be taken from some source of drinking water supply. The State Government can frame rules regarding the process of humidification etc.- Sec. 15.
Over Crowding :
There must be no overcrowding in a factory. In factories existing before the commencement of the Act there must be at least 350 of space per worker or factories built afterwards, there must be at least 500 c.ft. (or 75 cubic meters) of space. In calculating the space, an account is to be taken of space above 14 ft. (or 5 meters) from the floor.-Sec. 16.
Lighting :
Factories must be well lighted. Effective measures must be adopted to prevent glare or formation of shadows which might cause eyestrain.-sec. 17. It is the duty of the occupier to provide light.
Spittoons:
Every occupier should provide a sufficient number of spittoons in his factory at convenient places. The occupier may exhibit notices containing the prohibition of spitting within premises of the factory except in the spittoons and the penalty for the violation may also be imposed in that notice. Sec.20.
PROVISIONS REGARDING THE WELFARE OF WORKERS
Summary of the provisions of the Factories Act regarding the welfare of workers are stated below:
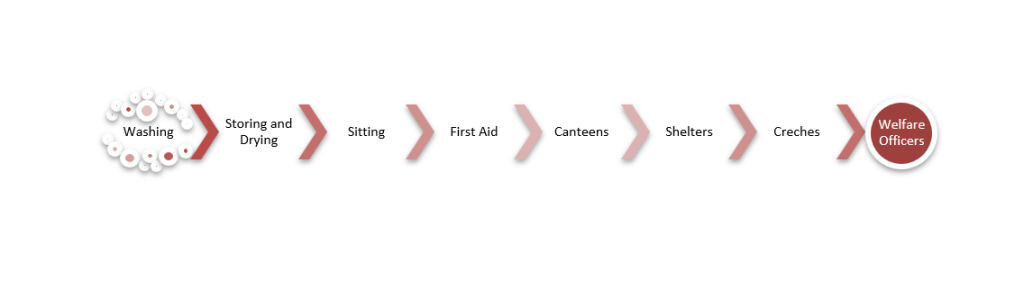
Washing. Sec. 42 :
In every factory adequate and suitable facilities for washing shall be provided and maintained. They shall be conveniently accessible and shall be kept clean. There must be separate provisions for male and female workers. Such facilities should be:-
- adequate and suitable
- maintained
- kept clean
- there shall be separate washing facilities for males and females with adequate screens, so that female shall enjoy privacy.
- Conveniently accessible.
Storing and drying. Sec. 43
The State Government may make rules requiring the provision of suitable facilities for storing and drying clothing.
- Keeping clothes not worn during working hours.
- For drying of wet clothing.
Sitting. Sec. 44
Sitting facilities must be provided for workers who have to work in a standing position so that they may take rest when possible. When work can be done in a sitting position efficiently the Chief Inspector may direct the provision of sitting arrangements.
First Aid. Sec. 45
Every factory must provide first aid boxes or cupboard. They must contain the prescribed materials and they must be in charge of persons trained in first aid treatment. Factories employing more than 500 persons must maintain an ambulance roam containing the prescribed equipment and in charge of the prescribed medical and nursing staff-5.
Canteens. Sec. 46
Where more than 250 workers are employed the state Government may require the opening of canteen or canteens for workers. Rules may be framed regarding the food served its management etc.
- the date by which such canteen shall be provided
- the standard in respect of construction, accommodation, furniture and other equipment of the canteen.
- The foodstuff to be served therein and the charges which may be made thereof.
Case law: Bengal W.P Walls us. State of Bengal (1970 Lab IC 71)
Issue: The question in this case arose was that whether employer was liable to run the canteen?
Judgment: The Court answered negatively. It is the State Government or The Chief inspector to make the appropriate rules for running the canteen by the managing committee. However the company should ensure the continuance of the canteen by providing the foodstuff or costs equivalent to them.
Shelters. Sec. 47
In every factory where more than 150 workers are employed there must be provided adequate and suitable shelters or rest. rooms and a lunch room (with drinking water supply) where workers may eat meals brought by them.
Such rooms must be sufficiently lighted and ventilated and must be maintained in a cool and clean condition.
The standards may be fixed by the State Government.
Creches. Sec. 48
In every factory where more than 30 women a employed, a room shall be provided for the use of the children (below 6 years) of such women. The room shall be adequate size well lighted and ventilated, maintained in a clean and sanitary condition and shall be in charge of a woman trained in the care of children and infants. The standards shall be laid down by the State Government.
Welfare officers. Sec. 49
Welfare officer must be appointed in every factory where 500 or more workers are employed. The State Government may prescribe the duties, qualifications etc. of such officers. 9. Rules. Sec. 50
The State Government may make rules regarding the welfare of workers.
____________________________________________________________________________________



