Collective Bargaining is a term adopted for the negotiation process between workers, represent by a Union such as a Trade Union, and their employer, represented by the management, for issues related to the terms and conditions of their employment such as wages, working hours, benefits, and workload. It has been provided in Industrial Relation Code 2020. An agreement arrived at by this negotiation process is called as Collective Bargaining Agreement (CBA) or Collective Employment Agreement (CEA).
Practically, a worker and his employer are not on an equal footing because of the financial power of the employer and as such, it is extremely difficult, if not impossible, for a single worker to pressure his employer to provide equitable benefits for his work. Historically, this has proven to be the main cause of dissatisfaction among workers, resulting in decreased productivity, and poor condition of workers. The objective of collective bargaining is to mitigate the disadvantage of economic disparity between the worker and the employer by bargaining with the employer collectively instead of individually.
Approaches to Collective Bargaining
1. Traditional or Positional or Adversarial or Distributional or Win-Lose Bargaining – In this type of bargaining both the parties, i.e. the union and the management, come out with their own agenda with little or no understanding of each others problems. The process mostly involves a give and take type of negotiation. This is the most common type of collective bargaining and is used all over the world.
2. Principled or Mutual Gains or Integrative or Win-Win Bargaining – In this type of bargaining both the parties understand the issues involved and they approach it to solve the problems jointly. Thus, an equitable solution without any acrimony can be found. This process works when there is not much disparity between the education level of both the parties, such as in IT industry.
The principle of collective bargaining is recognized by International Labor Organization (ILO) as well.
Bargaining Process
- The process starts with the workers uniting to form an association in the form of a Trade Union.
In the case of Workers of B and C Co vs Labour Commissioner, AIR 1964 Mad it was held that a Trade Union can raise or sponsor a trade dispute and represent on behalf of its members in legal proceedings arising out of a trade dispute. - Trade Union of registered and gets the power to represent the issues of the workers. Though it is not necessary for a TU to be registered. In the same case mentioned above, it was also held that an unregistered Trade Union that has the support of the majority of the workers has a better claim to negotiation than a recognized trade union that does not have majority support.
- The members of the trade union adopt a resolution to authorize the Trade Union to represent them and put their issues across to the management.
- Employer recognizes the Trade Union and gets ready to discuss the issues with the Trade Union representatives.
- The union representatives put their list of demands to the management and the management discusses those with the representatives.
- After a give and take either a mutually agreeable solution is found or pressurizing tactics such as strike or lock-out are adopted.
- If no solution is found, the matter could be referred to arbitration. If the solution is found, it is implemented and the process ends.
Benefits of Collective Bargaining
Benefits for Workers
- It provides uniformity and equality in conditions of labor for all laborers.
- It ensures progress of workers and increases their importance and respect.
- It prevents arbitrariness by owners regarding working conditions.
- It preserves personal interest of workers.
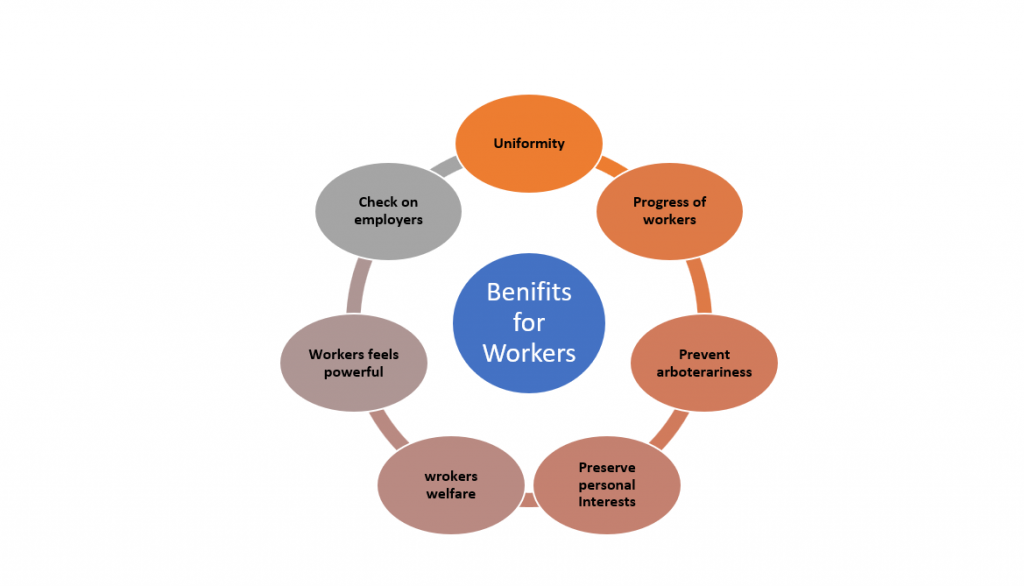
5. It promotes welfare of workers.
6. A worker does not feel alone and helpless, on the contrary, he feels powerful.
7. It provides a check on employers and inspectors.
Benefits for Employers
- It is cheaper, easier, and safer option.
- It saves time and it benefits all the parties equally.
- Compromises reached by this process are not only applicable to the parties but also to those who are not a party.
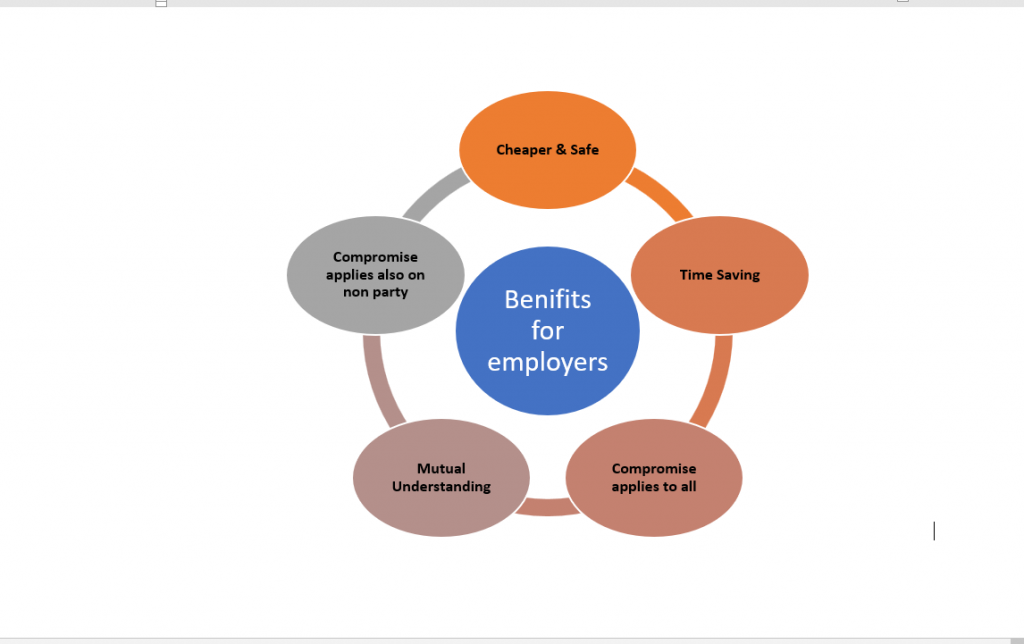
- Upon success of collective bargaining, industrial peace prevails and mutual understanding and production increases.
- Compromises done through collective bargaining are binding on all the parties.
Benefits in General
- Helps in satisfactory solution of problems and allows old customs and traditions.
- It reduces tension in parties and establishes a tradition of industrial peace.
- It has been proved helpful in bringing social change.
- Upon failure of the process, no party is insulted or hurt.
- In the case of Virundhachalam vs Management, Lotus Ltd, Lord Roland said that it ends the arbitrariness of inspectors by preventing them from becoming legal kings.



